Auto app discovery
The automatically generated KeptnApp file
aggregates the workloads to include in the application,
based on annotations made to the workloads themselves.
This enables you to run Keptn observability features on your cluster.
Afterward, you can monitor the status of the deployment using a command like the following:
The generated KeptnApp file includes metadata
that names this KeptnApp and identifies the Namespace where it resides.
It also includes a spec.workloads list
that defines the workloads to be included.
As an example, consider the following application, consisting of multiple deployments, which is going to be deployed into a Keptn-enabled namespace. Note that:
- Keptn is enabled for the namespace where your application runs.
- The
Deploymentworkloads are annotated appropriately. This example does not use other workloads.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: podtato-kubectl
annotations:
keptn.sh/lifecycle-toolkit: "enabled"
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: podtato-head-frontend
namespace: podtato-kubectl
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: podtato-head-frontend
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: podtato-head-frontend
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: podtato-head
app.kubernetes.io/version: 0.1.0
spec:
containers:
- env:
- name: PODTATO_COMPONENT
value: frontend
name: podtato-head-frontend
image: ghcr.io/podtato-head/podtato-server:v0.3.1
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: podtato-head-hat
namespace: podtato-kubectl
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: podtato-head-hat
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: podtato-head-hat
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: podtato-head
app.kubernetes.io/version: 0.1.1
spec:
containers:
- env:
- name: PODTATO_COMPONENT
value: hat
name: podtato-head-hat
image: ghcr.io/podtato-head/podtato-server:v0.3.1
Applying these resources results in the creation
of the following KeptnApp resource:
apiVersion: lifecycle.keptn.sh/v1
kind: KeptnApp
metadata:
name: podtato-head
namespace: podtato-kubectl
annotations:
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: "keptn"
spec:
version: "<version string based on a hash of all containing workloads>"
workloads:
- name: podtato-head-frontend
version: 0.1.0
- name: podtato-head-hat
version: 1.1.1
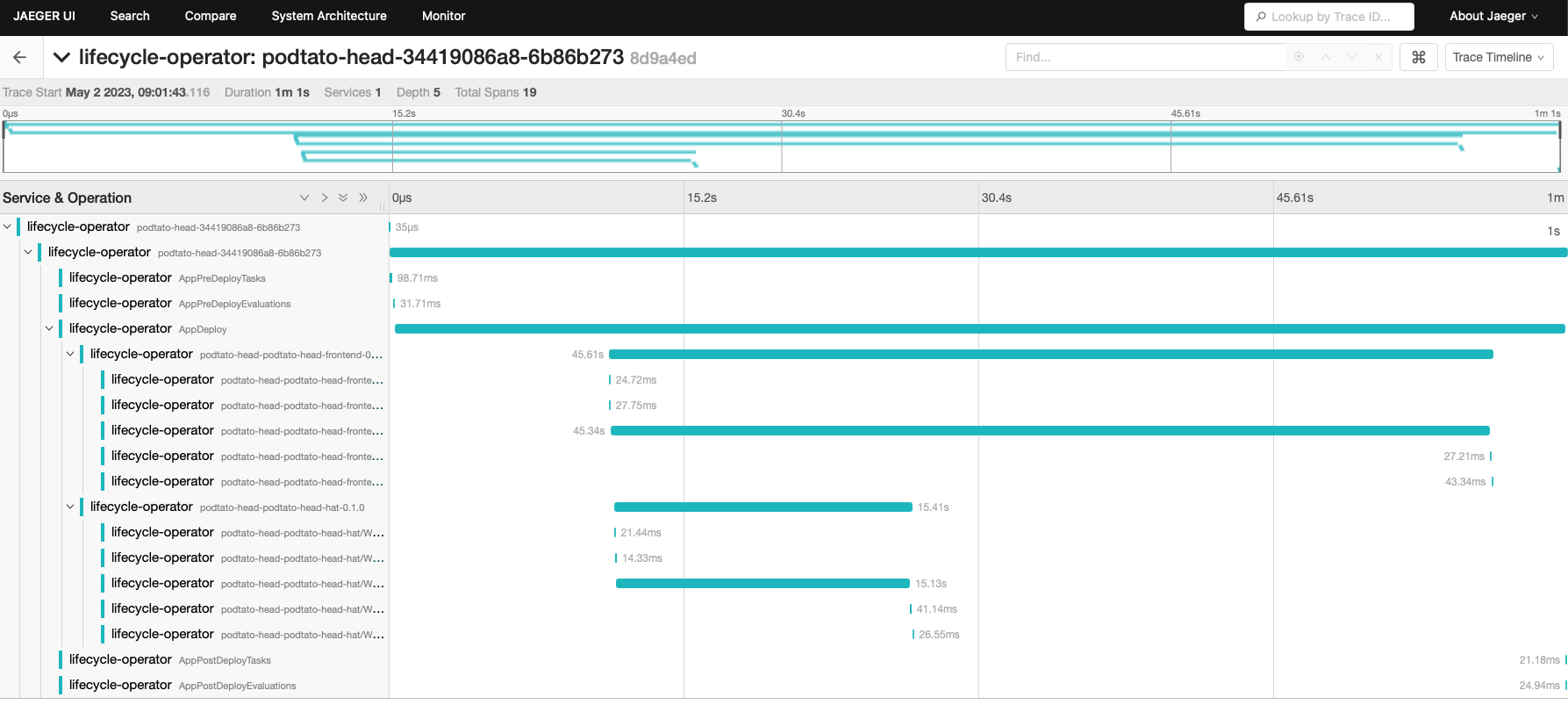
With the KeptnApp resource created,
you get observability of your application's deployments
by using the OpenTelemetry tracing features
that are provided by Keptn:
To execute pre-/post-deployment checks for a KeptnApp,
create a KeptnAppContext with the same name and in the same namespace as the KeptnApp.
The KeptnAppContext contains a list of
pre-/post-deployment tasks, evaluations, and promotion tasks
that should be executed before and after the
workloads within the KeptnApp are deployed.
See the Getting started guide
for more information on how to configure a KeptnAppContext
to execute pre-/post-deployment checks or promotion tasks.