Release Lifecycle Management
The Release Lifecycle Management tools run pre/post-deployment tasks and evaluations as well as promotion tasks for your existing cloud-native deployments to make them more robust. For more information, see Release lifecycle management.
This tutorial introduces these tools.
This tutorial assumes you have already completed the Getting started with Keptn Observability exercise. Please ensure you've finished that before attempting this exercise.
Keptn Pre and Post Deployment Tasks
When Keptn is successfully monitoring your deployments, it can also run arbitrary tasks and SLO evaluations for you either before or after your deployment runs. This is specified with labels or annotations in the Pod template specs of your workloads (Deployments, StatefulSets, DaemonSets, and ReplicaSets).
Pre and post deployments can be run either on individual workloads or on a group of associated workloads that are grouped into a
KeptnAppresource. For instructions about how to identify the workloads to combine intoKeptnAppresource, see annotations to KeptnApp. Auto app discovery explains how aKeptnAppresource is created.
Prerequisites: Deploy webhook sink
During this exercise, you will configure Keptn to trigger a webhook before and after a deployment has completed successfully.
For demo purposes, a place is required to which those requests are sent. To implement this:
-
Install the open source webhook.site tool.
This provides a place on your cluster to which web requests are sent and from which they can be viewed. If you have your own endpoint, you can skip this step.
-
Execute the following commands to apply the web hook:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/webhooksite/webhook.site/master/kubernetes/namespace.yml kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/webhooksite/webhook.site/master/kubernetes/redis.deployment.yml kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/webhooksite/webhook.site/master/kubernetes/laravel-echo-server.deployment.yml kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/webhooksite/webhook.site/master/kubernetes/webhook.deployment.yml kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/webhooksite/webhook.site/master/kubernetes/service.yml -
Wait until all Pods are running in the
webhooknamespace then port-forward and view the webhook sink page: -
Open a browser and go to
http://localhost:8084 -
You should see a page like this with a unique URL (your ID will be different than the example).
-
Make a note of that unique URL.
Verify Webhook Sink
Open a new browser table and go to your unique URL.
The page should remain blank, but when toggling back to http://localhost:8084, you should see a new entry.
Each request sent to that unique URL will be logged here.
Add a Post Deployment Task
Add a task that triggers after a successful deployment.
Change UUID to whatever value you have.
Apply this manifest:
apiVersion: lifecycle.keptn.sh/v1
kind: KeptnTaskDefinition
metadata:
name: send-event
namespace: keptndemo
spec:
retries: 0
timeout: 5s
container:
name: curlcontainer
image: curlimages/curl:latest
args: [
'-X',
'POST',
'http://webhook.webhook.svc.cluster.local:8084/YOUR-UUID-HERE',
'-H',
'Content-Type: application/json',
'-d',
'{ "from": "keptn send-event" }'
]
Verify it works
Verify that the KeptnTaskDefinition resource shown above actually works.
Trigger an on-demand task execution to verify that the job and Pod are working correctly.
In the following steps we have Keptn orchestrate this for us automatically.
Apply this manifest:
apiVersion: lifecycle.keptn.sh/v1
kind: KeptnTask
metadata:
name: runsendevent1
namespace: keptndemo
spec:
taskDefinition: send-event
context:
appName: "my-test-app"
appVersion: "1.0.0"
objectType: ""
taskType: ""
workloadName: "my-test-workload"
workloadVersion: "1.0.0"
If it works, kubectl -n keptndemo get jobs should show:
kubectl -n keptndemo get pods shows the successfully executed Pod.
The webhook sync should show this:
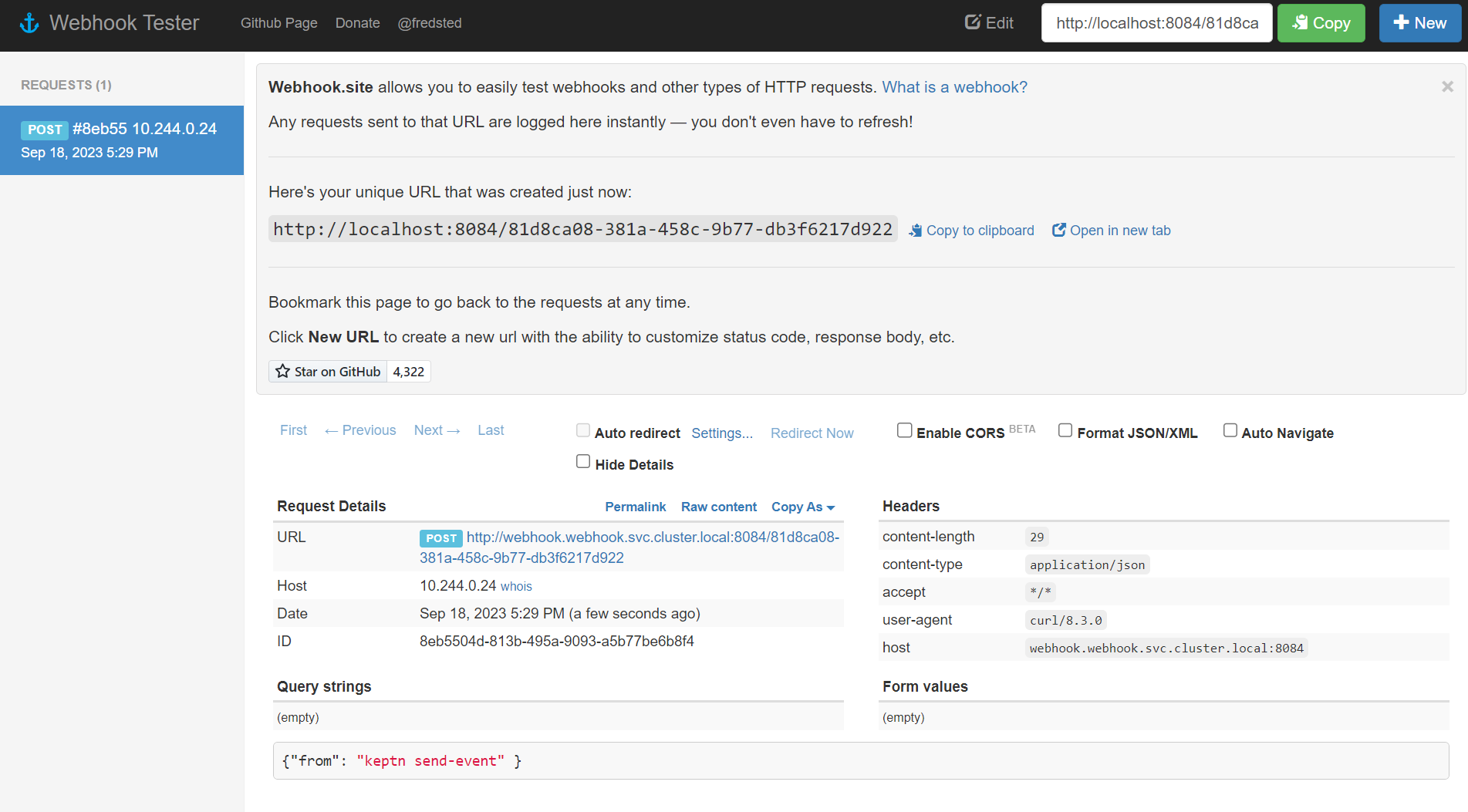
Incidentally, this is exactly how you can use Keptn with applications deployed outside of Kubernetes.
Note: If you want to trigger this task multiple times, you must change the value of the
namefield in theKeptnTaskresource each time. For example, changerunsendevent1torunsendevent2. See Redeploy/Restart an Application for details.
Ask Keptn to trigger task after Deployment
Annotate the demo application Deployment manifest
to have Keptn automatically trigger the task after every deployment.
Recall the Deployment from the
Observability
Getting started guide.
Add a new label so the labels section looks like this:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: keptndemoapp
app.kubernetes.io/name: nginx
app.kubernetes.io/version: 0.0.2
keptn.sh/post-deployment-tasks: "send-event"
Increase the version number to 0.0.2 and re-apply the manifest.
Here is a full version of the new YAML:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
namespace: keptndemo
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: keptndemoapp
app.kubernetes.io/name: nginx
app.kubernetes.io/version: 0.0.2
keptn.sh/post-deployment-tasks: "send-event"
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.14.2
ports:
- containerPort: 80
Best Practice: Start with post deployment tasks. Pre-deployment tasks can potentially block deployments (see below).
What Happens Next?
- The deployment is applied.
- When the Pods are running,
Keptn automatically creates a
KeptnTaskresource for version0.0.2of thisKeptnApp. - The
KeptnTaskcreates a KubernetesJob. - The Kubernetes
Jobcreates a KubernetesPod. - The
Podrunscurland sends a new event to the event sink.
Pre-deployment Tasks
Keptn Tasks can also be executed pre-deployment (before the Pods are scheduled).
Do this by using the keptn.sh/pre-deployment-tasks label or annotation.
Note: If a pre-deployment task fails, by default, the
Podremains in a Pending state.
More control over the application
To customize checks associated with the application, we can create a KeptnAppContext resource and define
a set of pre/post deployment tasks or evaluations as well as promotion tasks for the whole application.
Note that the name of the KeptnAppContext resource needs to match the name of the automatically
created KeptnApp and the value present in the keptn.sh/app or app.kubernetes.io/part-of
annotations.
In this case it needs to be keptndemoapp.
The KeptnAppContext also includes promotionTasks.
These are executed after the Deployment and all pre/post-deployment
tasks and evaluations are executed successfully.
They should serve only one purpose - to promote the application to another stage
(for example from dev to prod).
A promotion task is defined in a KeptnTaskDefinition resource:
apiVersion: lifecycle.keptn.sh/v1
kind: KeptnTaskDefinition
metadata:
name: promotion
namespace: keptndemo
spec:
deno:
inline:
code: |
console.log("Application promoted to stage prod!");
An example of KeptnAppContext executing post-deployment task send-event and
promotion task promotion:
apiVersion: lifecycle.keptn.sh/v1
kind: KeptnAppContext
metadata:
name: keptndemoapp
namespace: keptndemo
spec:
postDeploymentTasks:
- send-event
promotionTasks:
- promotion
This way, the send-event task is executed after the deployment of the whole application;
in other words, after all of the workloads present in the KeptnApp
are in a Running state.
After the send-event task succeeds, promotion task are executed.
A detailed description of all the available fields of the KeptnAppContext resource can be found in the
KeptnAppContext CRD reference page.
Note You must have the
promotionfeature enabled in order to execute promotion tasks. You can enable it vialifecycleOperator.promotionTasksEnabledhelm value during installation of Keptn. More information can be found here.
Further Information
You can do much more with KeptnTask resources.
See the
Deployment tasks
page to find out more.
To learn more about making pre-task and pre-evaluations non-blocking please see the Keptn non-blocking deployment section.
What's next?
Keptn can also run simple pre- and post-deployment SLO evaluations.
Continue the Keptn learning journey by adding evaluations. See the Evaluations for more information.